HYPERPIGMENTATION
What is it?
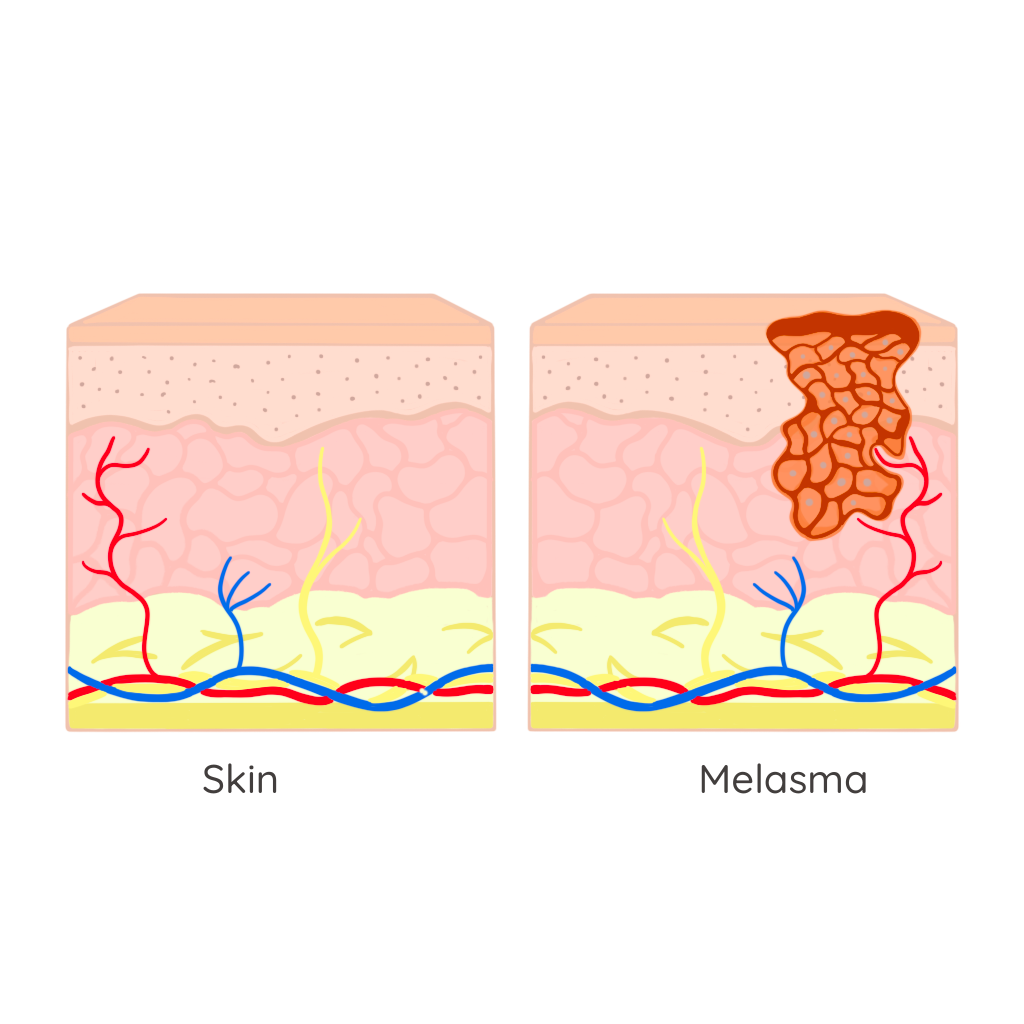
A common skin condition characterized by darkened areas or spots on the skin, resulting from an excess production of melanin. This condition can appear in various forms, including age spots, sun spots, and melasma, often influenced by factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, and inflammation. Hyperpigmentation can affect individuals of all skin types and tones, leading to uneven skin tone and a lack of uniformity in appearance. While it is not harmful, many seek ways to reduce its visibility for a clearer, more radiant complexion. Understanding hyperpigmentation is crucial for effectively addressing this issue and exploring suitable treatment options.
Key Facts
- Caused by Excess Melanin Production: Hyperpigmentation occurs when melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) produce too much melanin, leading to dark spots or uneven skin tone. [1]
- Triggered by Multiple Factors: Common causes include hormonal changes (like melasma), post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) from acne or injuries, aging, and certain medications. [2]
- Sun Exposure Worsens It: UV rays stimulate melanin production, making existing dark spots darker and causing new pigmentation to form. Daily SPF use is crucial for prevention and treatment. [3]
- Very Common: Hyperpigmentation is a common condition caused by regular environmental exposure. While sunscreen helps reduce the risk, most people will develop some degree of hyperpigmentation or uneven skin tone over time. [4]
How long does it last? Does it Relapse?
- Mild hyperpigmentation may fade in a few weeks, while deeper pigmentation (like melasma) may persist or start to grow.
- Even after successful treatment, hyperpigmentation can recur due to continued sun exposure, inflammation, or hormonal changes. Making maintenance and prevention essential.
- Mild post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) from acne or minor injuries can fade within a few weeks to months with proper care.
- Severe post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation may persist unless definitively treated.
- Melasma and deep pigmentation may take several months or even years to improve and often require ongoing treatment.
- Sunspots (age spots) can be long-lasting without professional treatment.
Is it curable or treatable?
- Different Types Require Different Treatments: Melasma, sunspots, and PIH each require different approaches, including chemical peels, laser therapy, microneedling, and brightening ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, and hydroquinone.
- Sun Protection Is Essential: Daily SPF use helps prevent new pigmentation and stops existing dark spots from worsening.
- Skincare Can Help Maintain Results: Brightening ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, kojic acid, and retinoids can keep skin clear and prevent relapse.
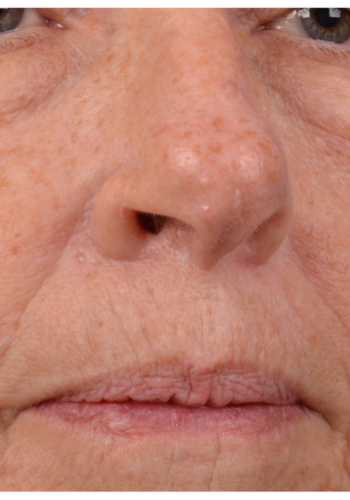
Before & After
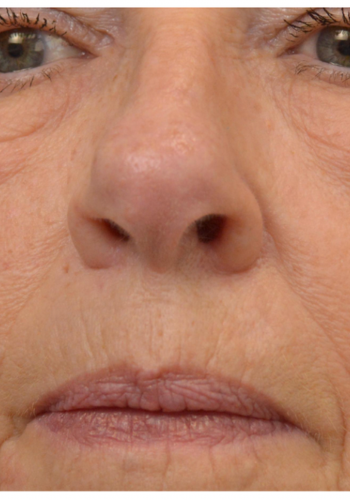


Our treatments
We combine medical and aesthetic expertise to create personalized skincare solutions using advanced laser and energy-based devices.

FAQ
Can hyperpigmentation go away on its own?
Mild cases, like post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), may fade over time, but deeper pigmentation, such as melasma or sunspots, often requires treatment for significant improvement.
What are the best treatments for hyperpigmentation?
Professional treatments like chemical peels, laser therapy, RF microneedling, and prescription creams (hydroquinone, retinoids, or vitamin C) can effectively reduce dark spots.
How long does it take to see results?
A: Professional treatments can speed up the process.
Mild hyperpigmentation can fade in a few weeks to months with consistent treatment.
Deeper pigmentation (like melasma) may take several months to improve.
Is hyperpigmentation bad?
Hyperpigmentation is a common, usually harmless condition in which patches of skin become darker in color than the normal surrounding skin.
Under rare circumstances hyperpigmentation may represent an underlying disease process which should be evaluated by a physician.