ROSACEA
What is it?
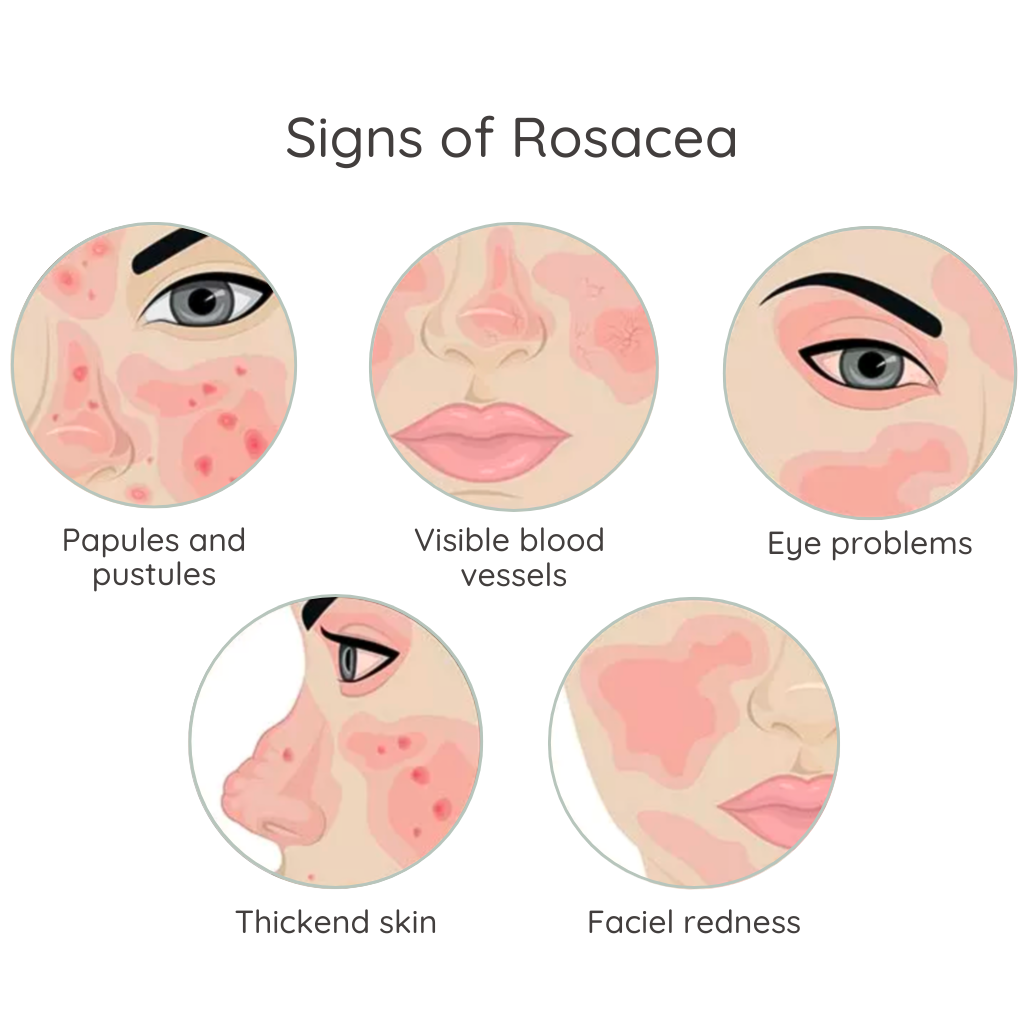
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition characterized by facial redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes small, pus-filled bumps. It commonly affects the central areas of the face, such as the cheeks, nose, and forehead, often leading to a flushed appearance. Triggers for rosacea can vary widely and may include sun exposure, stress, hot foods, alcohol, and temperature changes. While the exact cause of rosacea is not fully understood, it can be exacerbated by certain lifestyle factors and environmental conditions. Although rosacea is not harmful, it can affect self-esteem and quality of life. Understanding rosacea is essential for managing symptoms and exploring effective treatments to achieve a more even skin tone.
Key Facts
- Chronic Skin Condition with Flare-Ups: Rosacea is a long-term inflammatory skin condition that causes redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like bumps, mainly on the face. Flare-ups can come and go. [1]
- Triggers Worsen Symptoms: Common triggers include sun exposure, hot drinks, spicy foods, alcohol, stress, and extreme temperatures. Identifying and avoiding triggers can help manage symptoms. [2]
- Rosacea Is More Common in Certain People: It mostly affects fair-skinned individuals, especially those of Celtic or Northern European descent. However, it can occur in any skin tone and often appears between ages 30 and 50. [3]
- Not Contagious but Can Worsen Over Time: Rosacea is not an infection or contagious. But if left untreated, it can become more severe, leading to permanent redness, skin thickening, or eye irritation. [4]
- Rhinophyma is associated with Rosacea. Visit page here
How long does it last? Does it Relapse?
- Rosacea symptoms tend to come and go, with periods of remission followed by flare-ups triggered by factors like sun exposure, stress, spicy foods, alcohol, and weather changes.
- Topical medications, laser therapy, and lifestyle adjustments help keep symptoms under control and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
Is it curable or treatable?
- Medications Can Reduce Redness and Breakouts: Topical creams (like metronidazole, azelaic acid) and oral antibiotics help manage inflammation and acne-like bumps.
- Treatments Can Control Symptoms: While there is no cure, treatments like topical and oral medications, laser therapy, and skincare products can help reduce redness and flare-ups. Gentle skincare and daily sunscreen use are essential for managing rosacea.
- Laser and Light Therapy Can Improve Redness: Treatments like IPL (intense pulsed light) and laser therapy can reduce visible blood vessels and persistent redness.
- Skincare and Sun Protection Are Essential: Using gentle, fragrance-free skincare and daily sunscreen (SPF 30+) helps protect the skin and prevent flare-ups.
Before & After
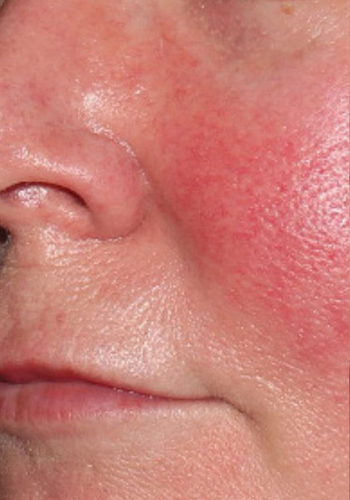
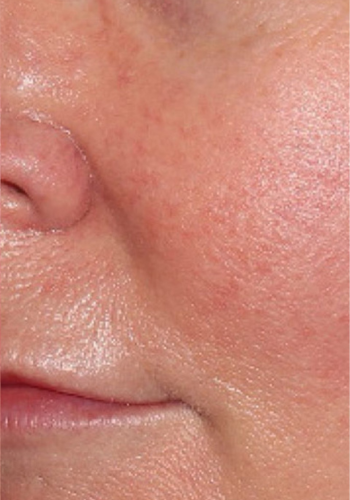


Our treatments
We combine medical and aesthetic expertise to create personalized skincare solutions using advanced laser and energy-based devices.

FAQ
Can Rosacea affect the eyes?
Yes, ocular rosacea can cause red, dry, irritated eyes and, in severe cases, lead to vision problems if left untreated.
Can diet affect rosacea?
Yes, certain foods and drinks—like spicy foods, alcohol, hot beverages, and caffeine—can trigger rosacea flare-ups in some people. Keeping a food diary can help identify personal triggers.
Is Rosacea Hyperpigmentation?
Rosacea is not hyperpigmentation. Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels. While hyperpigmentation results from excess melanin, leading to dark spots or patches. Hyperpigmentation is often caused by sun exposure, inflammation, or medications. Although they can coexist, they have different causes and treatments.
Can Rosacea just suddenly appear?
Yes, rosacea can appear suddenly, but it’s often caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors that have been building over time.